DESIGN SOLUTION
Analysis Recap
Based on our needs and learner analysis, we discovered that

Learning Goals and Objectives
Learning Goal: Learners will be able to confidently plan and cook healthy, time efficient meals using basic kitchen tools.
1. Students will apply foundational cooking skills to prepare quick, healthy meals using basic tools
- Students will list essential kitchen tools and ingredients needed to cook quick and healthy meals
- Students will select key ingredients and cooking techniques appropriate for a given recipe
- Students will apply learned cooking skills when following recipes and cooking tutorials
- Students will adapt five foundational cooking techniques (e.g., chopping vegetables, stir-frying, boiling grains, baking proteins, meal prepping) based on the tools and ingredients available to them
2. Students will make informed decisions about meal planning based on time, budget, and dietary needs
- Students will compare different meal prep and cooking methods to determine which method is the most time efficient
- Students will select budget-friendly, multi-use ingredients that align with personal dietary needs and minimize waste
- Students will design a personalized meal plan that aligns with their budget, time constraints, dietary restrictions, and preferences
3. Students will develop the motivation and confidence to cook regularly and sustain healthy eating habits
- Students will develop a sense of motivation to cook regularly by identifying personal goals and values related to health, time, and lifestyle
- Students will reflect on their cooking experiences to build confidence and recognize progress in their skill development
- Students will demonstrate increased self-efficacy by independently following recipes and preparing meals that align with their preferences and busy lifestyles
💡 Early Ideas
Explore the proposed solutions for empowering students to cook more confidently and efficiently. Click each idea to expand and learn more!

📱 Idea #1: Guided & Gamified Mobile Cooking Companion
a mobile application designed to guide busy college students through the process of planning and cooking healthy, time-efficient meals using basic kitchen tools.
Main Features:
- Short video tutorials (similar to YouTube and social media content that students already use) demonstrating recipes and cooking techniques.
- Interactive meal planning tools that allow students to input dietary needs, budget, and time constraints to generate recipe suggestions.
Rationale:
Faced by college students, offering quick and accessible cooking solutions via a familiar platform (mobile apps). The use of short video tutorials aligns with how students currently learn to cook (YouTube, social media), making the learning experience more engaging and less intimidating than traditional guides. Gamification can help to motivate students to cook regularly and develop healthy habits. The meal planning tools and recipe filters cater to the desire for budget-friendly meals requiring minimal equipment, and the step-by-step guides provide the necessary support for learners with varying levels of cooking confidence. By focusing on basic kitchen tools, it acknowledges the limited access to advanced appliances in dorms and shared apartments.
Pros:
- ✔ Customizable experience: having a tool where students are able to input their dietary restrictions and preferences helps in personalizing the experience for each learner.
- ✔ Engaging and accessible: the short video tutorials are easily accessible on a mobile device and the use of short videos keeps the learners engaged in the learning activity.
- ✔ User Control: short video tutorials allows the learner to control their experience by pausing or rewinding the video whenever they need to.
Cons:
- ✖ Lack of interactivity: Because the learners only follow the video tutorials, there is no way for the learners to ask questions or get immediate feedback from the instructor or chef.


🤖 Idea #2: Interactive and personalized cooking experience with AI chatbot support
This idea involves combining a skillshare type of video learning program with courses and recipes created by real chefs/experts, with an AI chatbot to support and customize the learning experience for the learners, teaching learners how to meal prep and cook recipes that are time efficient and personalized to their lifestyle and preferences.
Main Features:
- Several meal prepping and cooking video modules that the learners can choose from.
- Real chefs, available at designated times for feedback, or responses to submitted questions.
- An additional AI chatbot that can help assist them with immediate feedback, support or troubleshooting, and personalizing their experience.
Rationale:
From our analysis phase, we found that the problem wasn’t the learner’s ability to cook but their motivation and knowledge on cooking and meal prepping with significant time constraints from their busy college schedules. Because of this, I think creating a learning platform that still allows them to learn the basics of cooking and meal prepping while allowing them to also customize the experience to their personal lifestyle and preferences could help in improving their cooking skills and start being more mindful about the food that they eat, all while balancing their busy lifestyle.
Pros:
- ✔ Immediate assistance and customization: The use of an AI chatbot to assist the learner while the cook and offer customization options according to their preferences creates a more personalized experience for the learner.
- ✔ Interactive and Engaging: Being able to receive feedback from real chefs and getting assistance from the AI chatbot creates a more engaging learning experience that motivates the learner to continue learning.
Cons:
- ✖ Chefs limited availability: If students want to have a one-on-one feedback session with the chefs, their schedules might not align with each other.
- ✖ AI Limitations: There is always a risk that the information given by AI isn’t 100% accurate which can cause problems or delays in the learning activity.
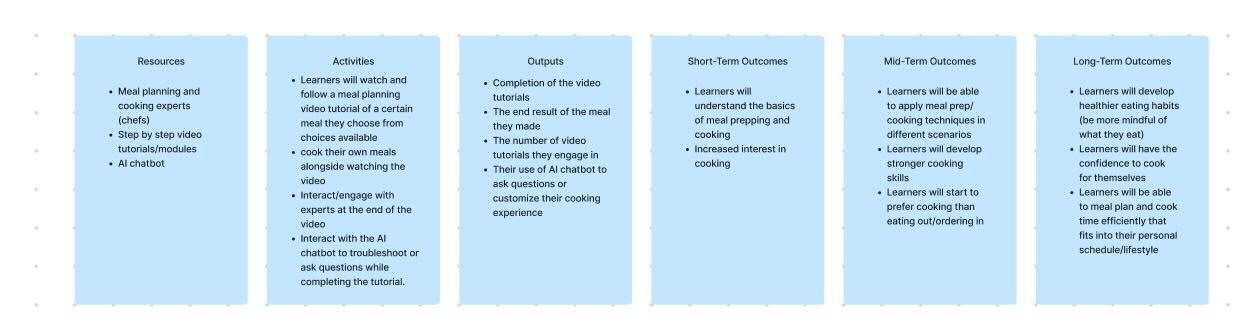

🎮 Idea #3: AR Cooking Game
It is an augmented reality cooking game designed , inspired by the popular cooperative game Overcooked. The game offers interactive, kitchen-based challenges that become progressively more complex, structured into clear levels of difficulty (Beginner, Intermediate, Advanced). Students engage individually and prepare virtual dishes in their own kitchens with limited time, guided by real-time AR visuals and instructions.
Main Features:
- Augmented Reality (AR): Overlays animated cooking tasks, recipe steps, timers, and tips directly onto the student’s real cooking environment.
- Gamified Interface: Levels, leaderboards, badges, and scoring systems to enhance motivation and competitive spirit.
- Interactive Tutorials: Step-by-step animated guidance for each cooking skill required at every level of difficulty.
- Timed Cooking Challenges: Encourages students to cook efficiently under pressure, mirroring real-life cooking scenarios.
Rationale:
Engaging and Immersive: The game-like AR environment significantly boosts learner engagement and motivation through a visually interactive and enjoyable cooking experience.
Progressive Skill Development: Clearly structured difficulty levels ensure learners gradually acquire and confidently build foundational skills before tackling advanced culinary challenges.
Real-Life Practicality: By using AR in their actual kitchens, students immediately translate digital instructions into real-world cooking skills.
Pros:
- ✔ Highly engaging and interactive: The game aspect is a fun way to motivate students to learn how to cook and would definitely keep them engaged in the learning activity.
- ✔ Immersive Experience: The use of AR creates an immersive experience for the learner so that they can actually participate in the activity as if they were actually cooking.
Cons:
- ✖ Doesn’t directly address problem: Although the game aspect is highly engaging and teaches the learners to cook under time constraints, because the learners would be creating a virtual dish, they aren’t actually learning how to cook.
- ✖ Time consuming: Because this game is virtual and the students aren’t actually cooking a real meal, this solution could actually be more time consuming because the learner would have to set aside time to play this game which can take time away from actually cooking.
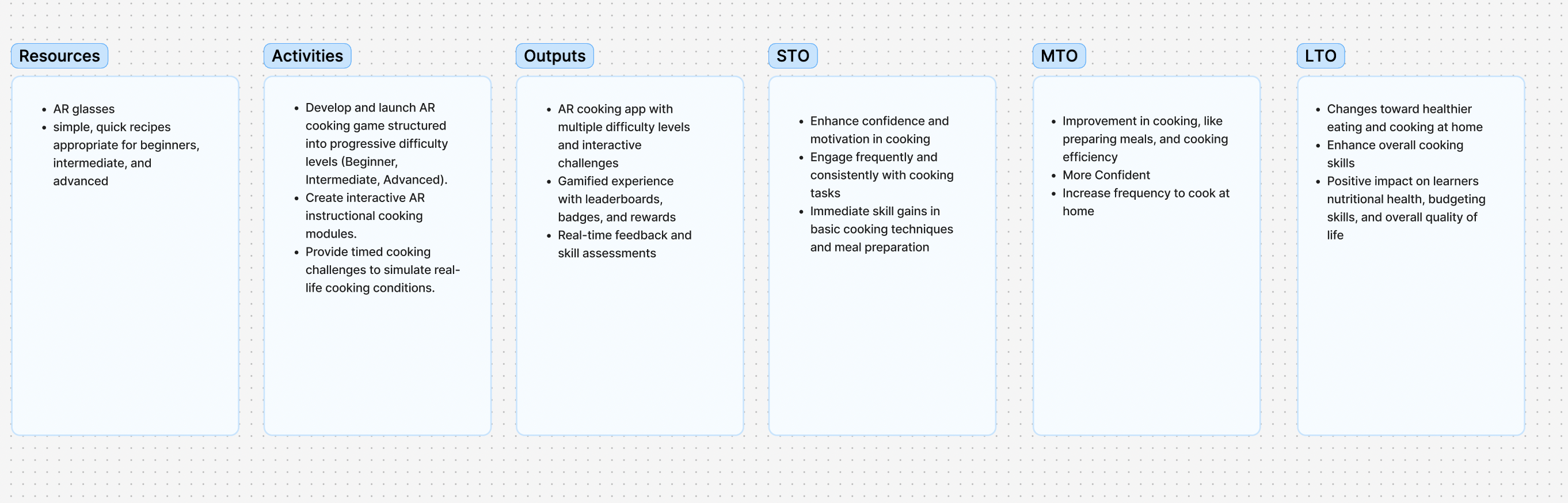

📊 Idea #4: Personalized Culinary Skill Development with AI Data Analysis
This idea centers around a platform that provides personalized culinary skill development for students through AI powered data analysis. The platform uses data collected from sensors and user input to tailor learning experiences. Students begin with a self assessment to determine their current skill level and cooking goals. Then, the platform recommends a series of learning modules including: instructional videos, interactive simulations, and virtual cooking challenges. As students engage with the modules, the platform tracks their progress, identifies areas for improvement, and provides targeted feedback and resources.
Main Features:
- AI-driven data analysis
- Interactive simulations
- Personalized video tutorials
- Virtual cooking challenges
Rationale:
This approach addresses the diverse skill levels and learning preferences of college students by offering a personalized learning experience. By using data analysis, the platform can pinpoint each student’s strengths and weaknesses, allowing for targeted instruction and efficient skill development. The virtual cooking challenges provide a safe and engaging environment for students to practice their skills and receive immediate feedback. Furthermore, the self-reflection prompts encourage students to think critically about their learning process and develop metacognitive skills. This method also provides a measurable way to track the student’s progress.
Pros:
- ✔ Personalized experience with AI data analysis: The use of AI analysis to track the learner’s progress creates a more tailored experience for them which can motivate the learner to learn to cook.
- ✔ Data-driven feedback: By receiving feedback from the AI analysis, the learner is able to pinpoint areas of improvement which helps them improve faster and more efficiently.
Cons:
-
✖ Lack of Human Feedback: Although the users receive feedback from AI, there isn’t an option to get feedback from real chefs on their cooking. AI also has the risk of being wrong and so the feedback given might not be accurate.
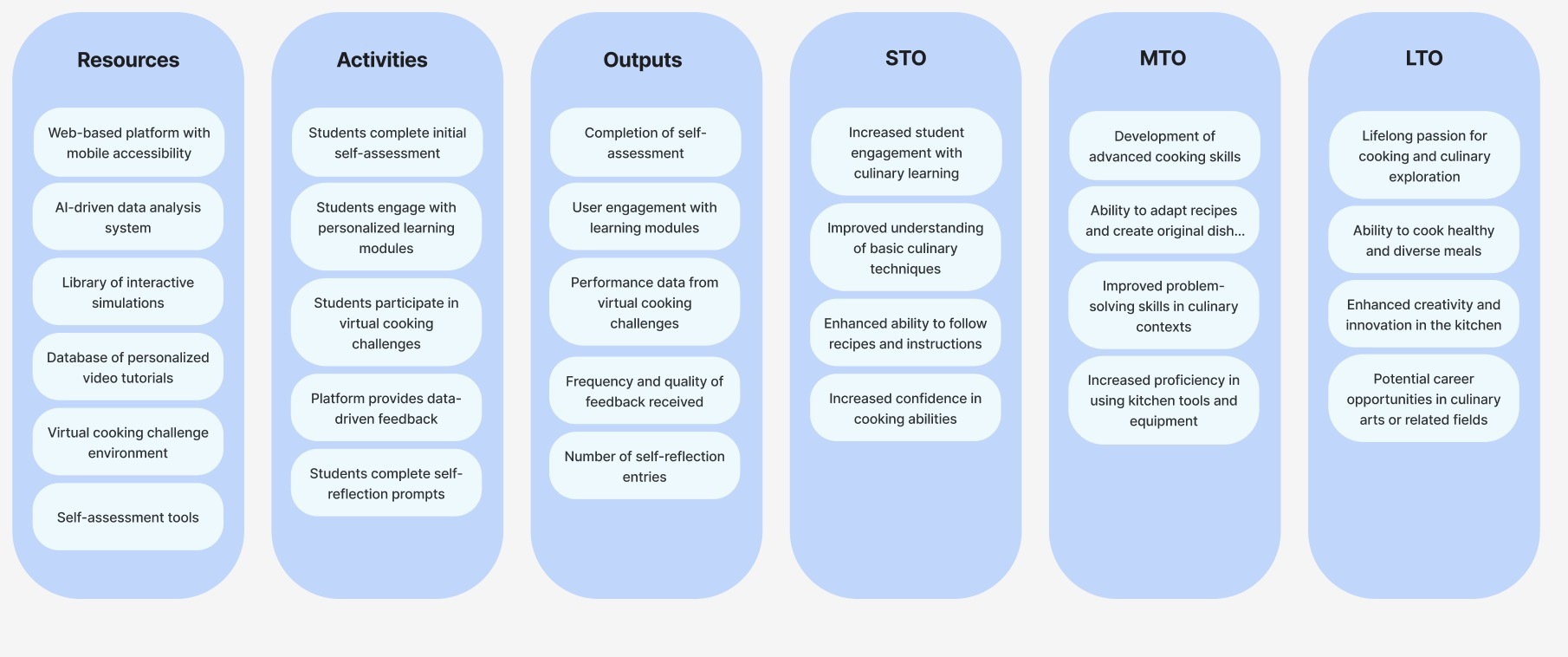

🎯 Final Learning Design Solution
Our final learning design solution is an intuitive and accessible mobile application that empowers learners to build cooking skills at their own pace. The platform offers a rich catalog of short, easy-to-follow video tutorials focused on recipes and meal planning. Learners receive a personalized experience through an interactive meal planning tool that tailors recipe suggestions based on their skill level, cooking goals, dietary needs, budget, and time constraints. AI-powered data analysis continuously tracks progress, identifies areas for growth, and delivers targeted feedback and recommendations. To further enhance the learning experience, users can share photos or videos of their completed dishes, ask questions, and receive direct feedback from professional chefs, creating an interactive and supportive learning experience.
Main Features:
- Short video tutorials: Cooking or meal planning tutorials are broken down into short tutorials that are quick enough to keep learners engaged in the content
- AI powered data analysis: tracks their progress and provides targeted feedback and recommendations
- Access to professional chefs: Learners can get feedback or ask questions to professional chefs to improve their cooking and meal planning skills
Delivery Method:
Primarily mobile application based
Learning Activities:
- Experiential Learning
Learning by doing; learners will cook alongside watching the short video modules - Interest-Driven Learning
Learners will be able to have a personalized experience through the interactive meal planning tool and AI data analysis
Learning Assessments:
- Self assessment
The learners can assess how they personally felt they did based on the meal they made or their meal prepping strategy - Informal assessment
Learners would get feedback from the AI data analysis and real chefs after the module is done, or answering questions from the comment section
Cooking Project Logic Model
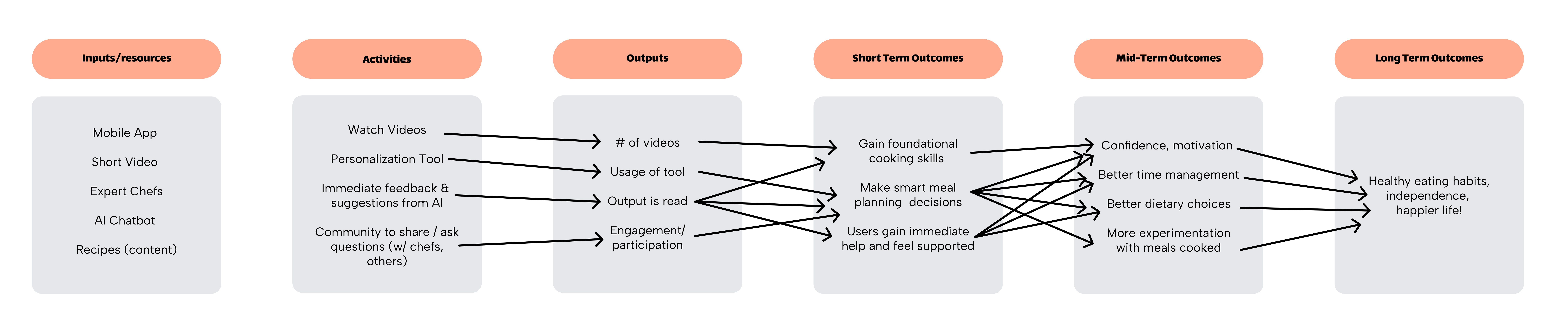
💡 Theory of Change & Design Rationale
Theory of Change
Need / Opportunity
College students often struggle to cook for themselves due to limited time, tight budgets, low confidence, and lack of experience. This app addresses these barriers by offering a personalized, engaging, and accessible learning experience.
After completing the learning experience, students will:
- Long-Term Goal: Students become nutritionally independent and sustain healthy, budget-conscious eating habits.
- Mid-Term Outcomes:
- Students consistently apply planning, budgeting, and cooking strategies in daily life.
- Students build habits and make better food decisions.
- Short-Term Outcomes:
- Students gain confidence in their cooking abilities.
- Students are able to prepare simple meals that match their dietary needs and time/budget constraints.
Activities + Design Rationale
| Feature / Activity | Supports the Outcome | Design Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Watch Videos (Short, engaging tutorials that model recipes and techniques) |
Builds baseline cooking skills and familiarity with basic tasks → Supports short-term outcome: students can cook simple meals | Dual Coding Theory (Paivio, 1986) + Multimedia Learning (Mayer, 2009): Combining video and audio improves understanding and recall |
| Use Personalization Tool (AI-driven path based on time, budget, dietary needs, goals) |
Keeps learning relevant and achievable → Supports mid-term outcome: consistent practice and better decision-making | Constructivism (Bruner) + ZPD (Vygotsky): Tailors learning to user's needs, maintaining optimal challenge |
| Receive Immediate Feedback & Suggestions from AI (After trying a recipe or completing a challenge) |
Encourages iteration and reflection → Supports both mid- and long-term outcomes through self-adjustment and learning from mistakes | Experiential Learning (Kolb, 1984): Learning through doing and reflecting builds skill competency |
| Participate in Community (Sharing meals, asking questions, learning from peers/chefs) |
Reinforces habit-building and motivation → Supports mid- and long-term outcomes: identity shift toward a self-sufficient, capable cook | Situated Learning (Lave & Wenger): Learning is social and contextual—community supports practice and belonging |
📝 Implementation Plan
🔹 Phase 1: Foundation and Self-Assessment
- Fill in a self-assessment questionnaire to set baseline skill levels and culinary objectives.
- See brief video tutorials on kitchen safety, basic tools needed, and fundamental skills.
- Participate in basic tasks of cooking like chopping vegetables or boiling pasta.
- Utilize in-app checklists to validate learning.
🛠️ Tools: Mobile app, 2–3 min videos, interactive check
🎯 Outcomes: Personal goals are understood, comfort with tools developed, basic capability
🔹 Phase 2: Practicing Skills under Feedback
- Get personalized recipe modules according to learner profile developed by AI.
- Follow interactive video tutorials that include embedded tips, timers, and practice guides.
- Post photos or videos of finished dishes for critique.
- Obtain feedback from the AI assistant or optional chef input.
🛠️ Tools: Recipe generator, video components, AI chatbot, interaction with a chef
🎯 Outcomes: Enhanced skill application, individualized correction, actual execution in the real world
🔹 Phase 3: Meal Planning and Application
- Utilize the meal planning tool to design a 3–5 day menu that meets goals and restrictions.
- Create a shopping list customized according to the plan.
- Fill in in-app reflective prompts related to learning confidence and time management.
- Optional: provide plan for feedback by a chef.
🛠️ Tools: Interactive planner, shopping list generator, reflection questions
🎯 Outcomes: Independent application, improved time/decision management, long-term habituation
📱 Delivery Form
The whole program is offered through a mobile application that is built for true asynchronous, self-directed learning. Students may learn whenever it suits them. Everything—the videos, the planning resources, and the AI analysis—works well on any smartphone.
Step-by-Step Implementation Flow
Step 1: Complete Self-Assessment
📋 Learners fill out a short questionnaire to identify current skills and cooking goals.
🛠️ Tool: In-app survey | 🎯 Output: Personalized learning path begins
Step 2: Watch Safety & Tools Videos
📋 Learners view short video tutorials on safety, knife handling, and basic equipment.
🛠️ Tool: 2–3 min videos | 🎯 Output: Awareness of kitchen basics
Step 3: Perform Basic Cooking Tasks
📋 Learners practice basic tasks like chopping vegetables or boiling pasta.
🛠️ Tool: Mobile app checklist | 🎯 Output: Confidence and readiness for next level
Step 4: Get AI-Personalized Recipe Modules
📋 Based on profile, learners receive suggested recipes and skill exercises.
🛠️ Tool: AI Recipe Engine | 🎯 Output: Targeted skill development
Step 5: Follow Interactive Cooking Tutorials
📋 Learners follow guided cooking sessions with embedded tips and timers.
🛠️ Tool: Interactive videos | 🎯 Output: Real-time practice
Step 6: Submit & Receive Feedback
📋 Learners upload dish photos/videos and receive AI or chef feedback.
🛠️ Tool: Submission portal + feedback chat | 🎯 Output: Skill refinement
Step 7: Create Meal Plan
📋 Learners design a 3–5 day meal plan according to personal needs.
🛠️ Tool: Interactive planner | 🎯 Output: Organized cooking schedule
Step 8: Generate Shopping List
📋 A shopping list is generated automatically based on chosen recipes.
🛠️ Tool: Grocery list generator | 🎯 Output: Budget and time efficiency
Step 9: Reflect and Adjust
📋 Learners reflect using prompts like "What worked well?" or "What was hard?"
🛠️ Tool: Reflection journal & dashboard | 🎯 Output: Long-term habit building
🧪 Learner Assessment
Our assessment strategy is designed to be continuous, reflective, and empowering—aligning with experiential learning theory and supporting learners in tracking their growth across skill, confidence, and habit formation.
🔍 Informal Evaluation
- Usage Data Tracking: The app monitors engagement metrics like module completion rates, time spent on activities, frequency of logins, and how consistently learners interact with different features. These analytics help identify patterns in user behavior and potential barriers to engagement.
- AI-Generated Feedback: After each cooking module or recipe tutorial, the AI assistant provides tailored suggestions—e.g., “Try a smaller dice on the carrots next time,” or “Well done following the timing steps!” This immediate, relevant feedback helps reinforce good habits while correcting mistakes in a non-judgmental manner.
- Weekly Progress Dashboards: Learners receive a personalized summary showing their progress across different skill domains, including recipe completion, challenge participation, and goal alignment. This visual reinforcement helps build motivation and shows clear milestones achieved.
🧠 Self-Assessment
- Reflective Prompts: After completing key activities, learners respond to prompts like “What did you find challenging about this task?” or “How would you improve your result next time?” This encourages metacognition and a growth mindset.
- Confidence and Skill Rating: Learners rate themselves using a 5-point scale (e.g., 1 = not confident, 5 = very confident) across categories such as “chopping,” “meal planning,” and “budget cooking.” This data informs future learning paths and helps learners see personal development over time.
- Visual Dashboard: Progress and reflection data are displayed on a personal dashboard, giving learners a quick overview of their growth and helping them set new goals. Optional notifications may prompt learners to revisit skills that haven’t been practiced recently.
💬 Peer and Optional Expert Feedback (Advanced Tiers)
- Community-Based Sharing: Learners can opt in to a private gallery to share photos or videos of completed dishes. Peers can leave comments or encouragement based on a rubric (e.g., visual appeal, creativity, effort).
- Chef Evaluation (Optional): For learners who want more structured feedback, the app may offer scheduled opportunities to submit videos for review by a professional chef. Feedback is framed around both technique and presentation.
🌱 Reflections on Project Development
Ruolin:
After the last presentation, I re-examined and modified parts of my previous task analysis. Visualizing each phase and mapping activities onto the timeline helped clarify what this stage should truly focus on—breaking down the learner’s tasks and aligning them with outcomes, instead of jumping directly to activities or assessments. This process provided me with a clearer direction for the next steps.
Working with George on the website layout made me realize how important collaboration is between different roles. I had to balance detailed content with how it would visually flow on the screen. This helped me prioritize clarity, consistency, and modularity—which are important.
George:
Creating the implementation plan pushed me beyond simply listing steps—it required me to critically analyze the logic and learner flow behind each phase. I realized that what sounds good on paper doesn’t always translate into actionable, learner-centered experiences. For example, I initially underestimated how difficult it is to balance learner autonomy with structured guidance. Planning this out forced me to think more deeply about sequencing: why a task must come first, what cognitive or motivational state it builds, and how it scaffolds the next step.
I also grappled with feasibility—imagining technical limitations, time constraints, and learner bandwidth, which are often overlooked in idealized designs. Through this process, I developed a stronger understanding of instructional practicality and how to design with both user behavior and system limitations in mind.
Nicole:
I really enjoyed this phase, as it gave us the opportunity to start ideating potential directions for our learning experience. The activities we worked on over the past few weeks, especially exploring different types of learning activities, assessments, and media tools, really pushed me to think more deeply and intentionally about each idea, rather than jumping to conclusions too quickly.
Creating logic models was especially helpful in evaluating the effectiveness of our ideas and identifying ways to improve them. Overall, it was exciting to see the range of ideas my group and I came up with, and interesting to notice how aligned we were in the end. It made it easy for us to come to a shared decision on what we felt was the strongest solution to address our learning problem.
Merry:
I realized the importance of putting learning theories into practice. For example, by applying DCT for the short video activity, it helps to give our design a more clarified path, and makes us think deeper from the user's side. It connected our ideas to learning theories that felt more rational and solid.
I liked making logic models the most, especially because of the activity we did in class. It gave me a clear structure of what I am doing and what should be done as the next step. For the next phase, I think it will be helpful to set small deadlines for specific tasks so we can move forward faster.
AI Acknowledgement
How AI Supported Our Design Section Development
AI Contributions:
- Generated layout ideas and supported the organization of content in the Design Section
- Polished written content to improve clarity, consistency, and professional tone
- Produced HTML structures and refined code for better visual presentation and user experience
- Generated AI-based images and visual assets to enhance the creativity and aesthetics of our ideas and prototypes
- Provided suggestions for improving accessibility and usability across devices
While AI tools were used extensively to support content writing, layout planning, image generation, and coding, the core ideas, decision-making, and creative direction of this project were led by our design team. Human judgement and collaboration played a central role in shaping and finalizing the work to reflect our vision and project goals.